Lets see the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE command as below
|
DELETE
|
TRUNCATE
|
|
DML Statement
|
DDL Statement
|
|
Data Rollback is possible, all the row by row data deletion will be recorded in transaction log
|
Rollback is possible for entire table and not at row level, since data page reallocation will be logged in transaction log
Eg.) BEGIN TRAN TRUNCATE Table Tablename ROLLBACK |
|
No Commit is performed neither before nor after. (Because it is a DML Statement)
|
It issues a COMMIT before it acts and another COMMIT afterward so no rollback of the transaction is possible. (Because it is a DDL Statement)
|
|
Row level locking will happen while performing deletion
|
Table level locking will be happen while performing truncation
|
|
A delete does not move the High Water Mark of the table back to zero, it retains its original position.
|
A truncate moves the High Water Mark of the table back to zero
|
|
WHERE statement can be included
|
WHERE statement cannot be included
|
|
Activates DML trigger
|
Doesnt activate DDL trigger
|
|
Able to execute the command on the table that contains foreign key
|
Not able to execute the command on the table that contains foreign key
|
|
Consume more resources since need to process row by row and all these are logged operation
|
Consume less resource since it will process the full table and its non-logged operation
|
Lets discuss the above points using an example
Consider you are holding a table TEST with the below schema
CREATE TABLE TEST(id INT IDENTITY(1,1), name VARCHAR(25))
INSERT TEST VALUES('naveen')
INSERT TEST VALUES('radha')
INSERT TEST VALUES('shilpa')
INSERT TEST VALUES('govind')
INSERT TEST VALUES('mark')
The full table internal allocation is shown below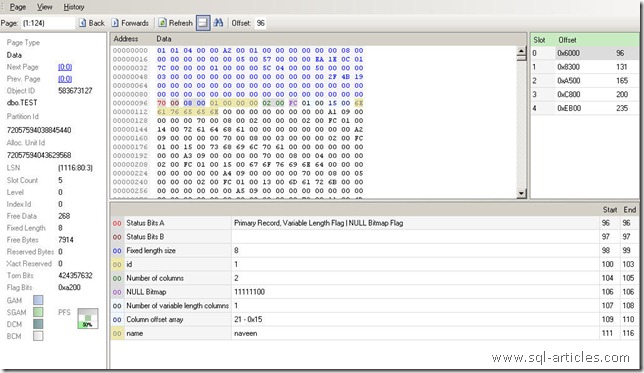
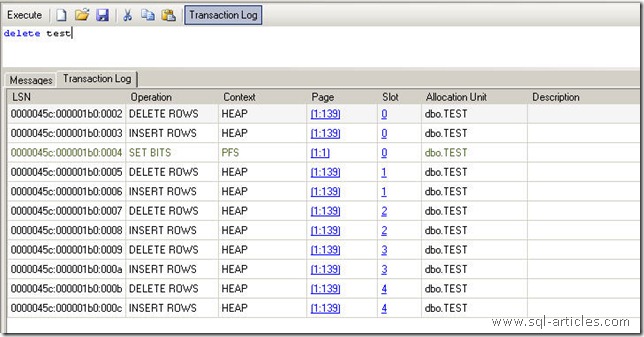
When you issue a DELETE command it will process the data deletion row by row, you can see the transaction log as below
DELETE TEST
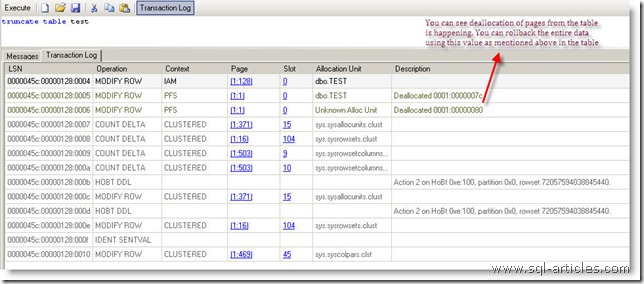
As said earlier when you issue and TRUNCATE command it will deallocate the page from the table hence its faster than delete command, check out the below picture
TRUNCATE TABLE TEST
When you use DELETE command it does not move the High Water Mark of the table back to zero, consider you are deleting row 3 and inserting a new row , from the below image you can check the ID is pointed to 6
DELETE TEST WHERE id=3
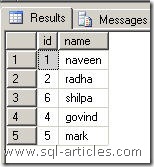
INSERT TEST VALUES('shilpa')
When you use TRUNCATE command it moves the High Water Mark of the table back to zero and hence the ID column will be reset again, check the below pic
INSERT TEST VALUES('naveen')
INSERT TEST VALUES('radha')
INSERT TEST VALUES('shilpa')
INSERT TEST VALUES('govind')
INSERT TEST VALUES('mark')
You can drop the table using DROP TABLE TEST command
Conclusion:
I hope the above article will provide you the differences between DELETE and TRUNCATE command.
Leave a Reply